dynadojo.systems.lds.LDSystem#
- class dynadojo.systems.lds.LDSystem#
Bases:
SimpleSystemLinear dynamical system (LDS). Implements an LDS of the form \(\dot{x} = Ax + Bu\) where \(Ax\) is the drift term of \(\dot{x}\) and \(Bu\) is input term of \(\dot{x}\).
Example
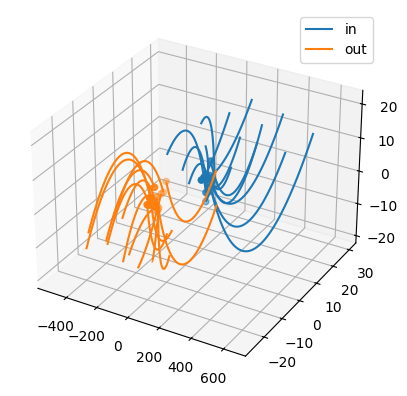
>>> from dynadojo.systems.lds import LDSystem >>> from dynadojo.wrappers import SystemChecker >>> from dynadojo.utils.lds import plot >>> latent_dim = 9 >>> embed_dim = 14 >>> n = 500 >>> timesteps = 50 >>> system = SystemChecker(LDSystem(latent_dim, embed_dim, noise_scale=0, seed=0)) >>> x0 = system.make_init_conds(n) >>> y0 = system.make_init_conds(30, in_dist=False) >>> x = system.make_data(x0, timesteps=timesteps) >>> y = system.make_data(y0, timesteps=timesteps, noisy=True) >>> plot([x, y], target_dim=min(latent_dim, 3), labels=["in", "out"], max_lines=15)
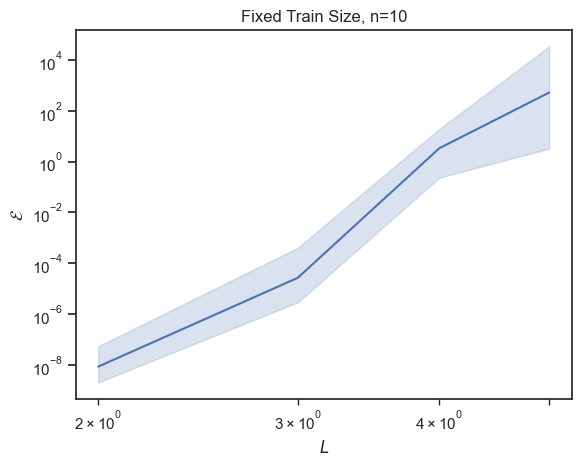
>>> from dynadojo.baselines.dmd import DMD >>> from dynadojo.challenges import FixedTrainSize >>> challenge = FixedTrainSize(L=[2, 3, 4, 5], E=None, t=50, n=10, reps=10, system_cls=LDSystem, test_examples=1, test_timesteps=50, max_control_cost_per_dim=0, control_horizons=0) >>> data = challenge.evaluate(algo_cls=DMD) >>> challenge.plot(data)
Methods
__init__([latent_dim, embed_dim, ...])Initialize the class.
calc_control_cost(control)Calculates the L2 norm / dimension of every vector in the control
calc_dynamics(t, x)Calculates the dynamics for the system.
calc_error(x, y)Returns the MSE error normalized by the embedded dimension.
make_data(init_conds, control, timesteps[, ...])Uses the
calc_dynamics()method to generate data.make_init_conds(n[, in_dist])Uniformly samples embedded-dimensional points from an inside or outside distribution
Attributes
The controller matrix.
The embedded dimension for the system.
The embedder matrix.
The latent dimension for the system.
The random seed for the system.
- __init__(latent_dim=2, embed_dim=2, A_eigval_range=(-1, 1), A_eigvec_range=(-1, 1), **kwargs)#
Initialize the class.
- Parameters:
latent_dim (int, optional) – Dimension of the latent space. Defaults to 2. Can set to large values.
embed_dim (int, optional) – Embedded dimension of the system. Defaults to 2. Can set to large values. Should be at least as large as latent_dim.
A_eigval_range (tuple, optional) – Range for eigenvalues of the matrix A. Defaults to (-1, 1). Recommended to keep this value between -1 and 1 for stable systems.
A_eigvec_range (tuple, optional) – Range for eigenvectors of the matrix A. Defaults to (-1, 1).
**kwargs – Additional keyword arguments.
- calc_control_cost(control)#
Calculates the L2 norm / dimension of every vector in the control
- Parameters:
control (ndarray) –
- Return type:
float
- calc_dynamics(t, x)#
Calculates the dynamics for the system. Your class must implement this.
- calc_error(x, y)#
Returns the MSE error normalized by the embedded dimension.
- Return type:
float
- property controller#
The controller matrix. For example, in a system \(\dot{x} = Ax + Bu\), the controller is \(B\).
- property embed_dim#
The embedded dimension for the system.
- property embedder#
The embedder matrix. An invertible map from the latent space to the embedding space.
- property latent_dim#
The latent dimension for the system.
- make_data(init_conds, control, timesteps, noisy=False)#
Uses the
calc_dynamics()method to generate data. Mathematically, data is generated like \(\dot{x} = f(x) + Bu\). Where \(f(x)\) is given bycalc_dynamics().- Parameters:
init_conds (numpy.ndarray) – (n, embed_dim) Initial conditions matrix.
control (numpy.ndarray) – (n, timesteps, embed_dim) Controls tensor.
timesteps (int) – Timesteps per training trajectory (per action horizon).
noisy (bool, optional) – If True, add noise to trajectories. Defaults to False. If False, no noise is added.
- Returns:
(n, timesteps, embed_dim) Trajectories tensor.
- Return type:
numpy.ndarray
- make_init_conds(n, in_dist=True)#
Uniformly samples embedded-dimensional points from an inside or outside distribution
Note
Systems developers determine what counts as in vs out-of-distribution. DynaDojo doesn’t provide any verification that this distinction makes sense or even exists. See
LDSystemfor a principled example.- Parameters:
n (int) – Number of initial conditions.
in_dist (bool, optional) – If True, generate in-distribution initial conditions. Defaults to True. If False, generate out-of-distribution initial conditions.
- Returns:
(n, embed_dim) Initial conditions matrix.
- Return type:
numpy.ndarray
- property seed#
The random seed for the system.