dynadojo.baselines.dmd.DMD#
- class dynadojo.baselines.dmd.DMD#
Bases:
AbstractAlgorithmDynamic mode decomposition. Implementation uses the
pydmdlibrary [1].Note
For an example of
DMDwith a challenge, seeLDSystem.References
Example
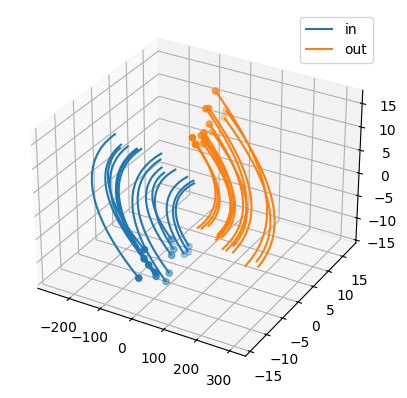
from dynadojo.systems.lds import LDSystem from dynadojo.wrappers import SystemChecker from dynadojo.utils.lds import plot latent_dim = 3 embed_dim = 10 n = 15 timesteps = 20 system = SystemChecker(LDSystem(latent_dim, embed_dim, noise_scale=0, seed=2)) x0 = system.make_init_conds(n) y0 = system.make_init_conds(30, in_dist=False) x = system.make_data(x0, timesteps=timesteps) y = system.make_data(y0, timesteps=timesteps, noisy=True) plot([x, y], target_dim=min(latent_dim, 3), labels=["in", "out"], max_lines=15)
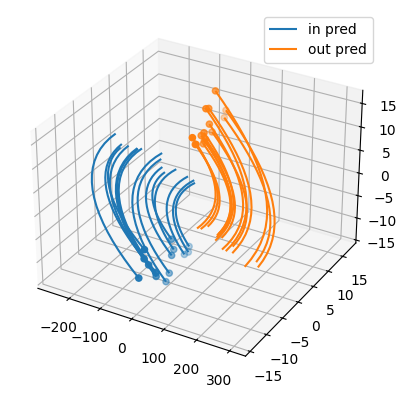
from dynadojo.baselines.dmd import DMD from dynadojo.wrappers import AlgorithmChecker dmd = AlgorithmChecker(DMD(embed_dim, timesteps, activation=None, max_control_cost=0)) dmd.fit(x) x_pred = dmd.predict(x[:, 0], timesteps) y_pred = dmd.predict(y[:, 0], timesteps) plot([x_pred, y_pred], target_dim=min(3, latent_dim), labels=["in pred", "out pred"], max_lines=15) x_err = system.calc_error(x, x_pred) y_err = system.calc_error(y, y_pred) print(f"{x_err=}") print(f"{y_err=}")
Both errors should be around 0 and the predictions looks like this:
Methods
__init__(embed_dim, timesteps[, ...])Initialize the class.
act(x, **kwargs)Determines the control for each action horizon.
fit(x, **kwargs)Fits the algorithm on a tensor of trajectories.
predict(x0, timesteps, **kwargs)Predict how initial conditions matrix evolves over a given number of timesteps.
Attributes
The embedded dimension of the dynamics.
The maximum control cost.
The random seed for the algorithm.
The timesteps per training trajectory.
- __init__(embed_dim, timesteps, max_control_cost=0, **kwargs)#
Initialize the class.
- Parameters:
embed_dim (int) – Recommended embedding dimension should be <5.
timesteps (int) – Timesteps in the training trajectories.
max_control_cost (float) – Ignores control, defaults to 0.
**kwargs – Additional keyword arguments.
- act(x, **kwargs)#
Determines the control for each action horizon. control.
- Parameters:
x (numpy.ndarray) – (n, timesteps, embed_dim) Trajectories tensor.
**kwargs – Additional keyword arguments.
- Returns:
(n, timesteps, embed_dim) controls tensor.
- Return type:
numpy.ndarray
- property embed_dim#
The embedded dimension of the dynamics.
- fit(x, **kwargs)#
Fits the algorithm on a tensor of trajectories.
- Parameters:
x (np.ndarray) – (n, timesteps, embed_dim) Trajectories tensor.
**kwargs – Additional keyword arguments.
- Return type:
None
- property max_control_cost#
The maximum control cost.
- predict(x0, timesteps, **kwargs)#
Predict how initial conditions matrix evolves over a given number of timesteps.
Note
The timesteps argument can differ from the ._timesteps attribute. This allows algorithms to train on a dataset of a given size and then predict trajectories of arbitrary lengths.
Note
The first coordinate of each trajectory should match the initial condition x0.
- Parameters:
x0 (np.ndarray) – (n, embed_dim) initial conditions matrix
timesteps (int) – timesteps per predicted trajectory
**kwargs – Additional keyword arguments.
- Returns:
(n, timesteps, embed_dim) trajectories tensor
- Return type:
np.ndarray
- property seed#
The random seed for the algorithm.
- property timesteps#
The timesteps per training trajectory.